|
|
Sponsored Content
The Lounge
What is on Your Mind?
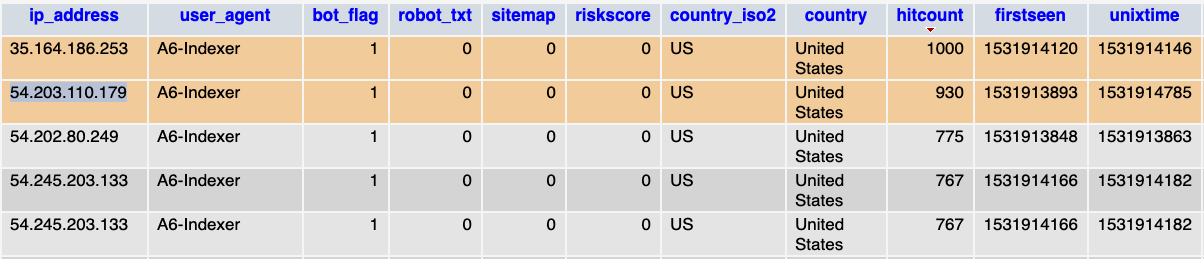
Blocked A6-Index and Entire AWS Netblock
Post 303020391 by Neo on Wednesday 18th of July 2018 08:00:35 AM
|
|
7 More Discussions You Might Find Interesting
1. IP Networking
Due to the massive Upload speeds killing .... or overstressing our schools network...... my school has blocked port 6969 (the most common BitTorrent port). So I cant connect to the tracker anymore, in other words no more downloading from school :(
Does anyone know how I can get around the ports... (1 Reply)
Discussion started by: PenguinDevil
1 Replies
2. Filesystems, Disks and Memory
why do inode indices starts from 1 unlike array indexes which starts from 0
its a question from "the design of unix operating system" of maurice j bach
id be glad if i get to know the answer quickly
:) (0 Replies)
Discussion started by: sairamdevotee
0 Replies
3. UNIX for Dummies Questions & Answers
brothers why inode index starts from 1 unlike array inex which starts from 0
its a question from the design of unix operating system of maurice j.bach
i need to know the answer urgently...someone help please (1 Reply)
Discussion started by: sairamdevotee
1 Replies
4. Shell Programming and Scripting
Hi All,
I have a file (FileNames.txt) which contains the following data in it.
$ cat FileNames.txt
MYFILE17XXX208Sep191307.csv
MYFILE19XXX208Sep192124.csv
MYFILE20XXX208Sep192418.csv
MYFILE22XXX208Sep193234.csv
MYFILE21XXX208Sep193018.csv
MYFILE24XXX208Sep194053.csv... (5 Replies)
Discussion started by: krish_indus
5 Replies
5. Virtualization and Cloud Computing
Tim Bass
07-25-2008 02:34 AM
The admin*team at The UNIX Forums*have been considering moving the UNIX and*Linux*Forums to the clouds - the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud.* Amazon EC2 is one option to scale the forums, which is a*LAMP application.*
Amazon EC2 allows*us to rent dedicated... (3 Replies)
Discussion started by: Linux Bot
3 Replies
6. Shell Programming and Scripting
Hello All,
I am trying few stuff on Amazon S3 move files to EC2 (Ubuntu Server)
I am receiving daily 2 files in S# bucket
XYZ_2015-02-26_ 200.csv
ABC_2015-02-26_ 200.csv
I want to move daily received files to local EC2(Ubuntu server) and rename files to
XYZ_2015-02-26.csv... (3 Replies)
Discussion started by: krux_rap
3 Replies
7. Shell Programming and Scripting
2 scripts to convert IP ranges to CIDR notation using awk, gawk or mawk. The scripts are much faster than using ipcalc and will return the same results. The first script is reliably compatible with awk, gawk and mawk but is over 3 times as slow as the second script which is reliably compatible with... (38 Replies)
Discussion started by: azdps
38 Replies
LEARN ABOUT DEBIAN
gpiv_combing
GPIV_COMBING(1) General Commands Manual GPIV_COMBING(1) NAME
gpiv_combing - Combines two single-exposed images into one image file for cross-correlation. SYNOPSIS
gpiv_combing [-a | --suf_a S] [-b | --suf_b S] [-d | --dt S] [-h | --help] [-p | --print] [-s | --skip S] [-t | --type] [-u | --suf_num N] [-v | --version] [-V | --verbose] [-w | --warning] file_basename DESCRIPTION
gpiv_combing combines two images from a common image format that use lossless compressing schemes into a Portable Network Graphics image with extension .png. The resulting 'double frame' image is used for cross-correlation with gpiv_rr (or gpiv). Additional information is added to the image header, like the parameter for enabling cross correlation, separation time between the recordings of the two images and the name of this program. This program uses the IMG configuration parameters. As the input images are single-frame and will probably not contain the required X_corr parameter in its header, the IMG.X_corr setting will have to be set to 0 for the correct loading. The default settings may be overruled by the command line options, as explained below. Options -h | --help On-line help. -a | --suf_a S The filename of the first image is generated from the file_basename, the suffix S (default: _a) and from the image extension type. -b | --suf_b S The filename of the second image is generated from the file_basename, the suffix S (default: _b) and from the image extension type. -d | --dt S The time between subsequent images in milliseconds. The value will be written to the image header. If -s | --skip is used, the sepa- ration time will be adapted to the correct value. -p | --print Prints parameters to stdout. -s | --skip S Skip S numbers; the first image with number N (defined by -u | --suf_num N) will be combined with the second image N+S+1 (default: S = 0) -t | --type Type or format of the input image (default png). Supported formats are: raw binary (r), hdf5 (gpi), gif, tif, bmp and pgm. The for- mat of the output image will always be png. -u | --suf_num N If images are numbered instead of having suffixes _a and _b. N represents the first of the two numbered frames which will be com- bined with frame N + 1. The combined image will be named to file_basenameN.png. So, only odd or even numbered images will result to be loaded in gpiv_rr (or gpiv) for cross-correlation. -v | --version Print version information on standard output, then exit successfully. -V | --verbose Program behaves verbose during operation, like printing filenames, separation time. -w | --warning Checks and warns if one of the two input images already contain an image pair, i.e. the header parameter X-corr is set TRUE. The program will exit if this is the case. Besides this warning, the program will always check if the images are of equal sizes. If an input image does not contain the X-corr parameter in its header, the parameter will be read from the parameter resources. Not using this option allows one to keep the settings in the parameter resources in any state. file_basename The filename without the image extension (like .png, .tif etc) and suffix or number. Examples Suppose two single-exposed images will have to be combined for cross-correlation with names image_a.gif and image_b.gif: so the file_base- name will be "image", _a and _b are default suffixes and the image type has to be defined. The program is used following: gpiv_combing -t gif image As PNG is default image format, -t key is not needed. Two images with names turtle_slow.png and turtle_fast.png are combined with: gpiv_combing -a _slow -b _fast turtle For two numbered images img03.png and img04.png only the starting number will have to defined: gpiv_combing -u 3 img0 Two numbered images img03.png and img09.png will have to be combined by skipping 5 images in-between. If -d | --dt S is used, the correct separation time between the combined frames is calculated from S: gpiv_combing -u 3 -s 5 img0 SEE ALSO gpivtools NOTES
The program uses netpbm. AUTHOR
Gerber Van der Graaf 31 October 2006 GPIV_COMBING(1)